Diabetes is affecting about 422 million people worldwide living in low-and middle-income countries. Each year, 1.6 million deaths are directly attributed to it. Its prevalence has continuously increased over the past decades and is estimated to keep on rising (World Health Organization, 2020).
Diabetes has become a common lifestyle disease that leads to blindness, limb amputation, diabetic ketoacidosis, and other complications brought about by organ failure and eventually to death. But with advances in technology, diabetes has become manageable and curable.
What Is Diabetes Management?
Diabetes management is simply living with diabetes through regular checking of blood sugar levels. In this way, the risks of developing enduring complications are decreased. It is a continuous assessment that ensures diabetic patients from unprecedented health risks. It also supplies valuable information to the doctor on what adjustments to make in the whole care plan.
How Do You Manage Diabetes?
Experts from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases mentioned four ways to manage diabetes for life:
- Learn about diabetes
- Know your diabetes
- Learn how to live with diabetes
- Get routine care to stay healthy. You can visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for more details.
These 4 ways are confirmed by Dowshen (2018), that managing diabetes is similar to a three-way balancing act of medicines you take, the food you eat, and the amount of exercise you get, synch together. In other words, your lifestyle and daily routine have a connection with your sugar levels. Controlling them makes a lot of difference in your life.
On the other hand, diabetes technology has made these activities more effortless and comfortable. Several items can help you manage diabetes better.
What Are Indispensable Items Diabetic Patients Should Own?
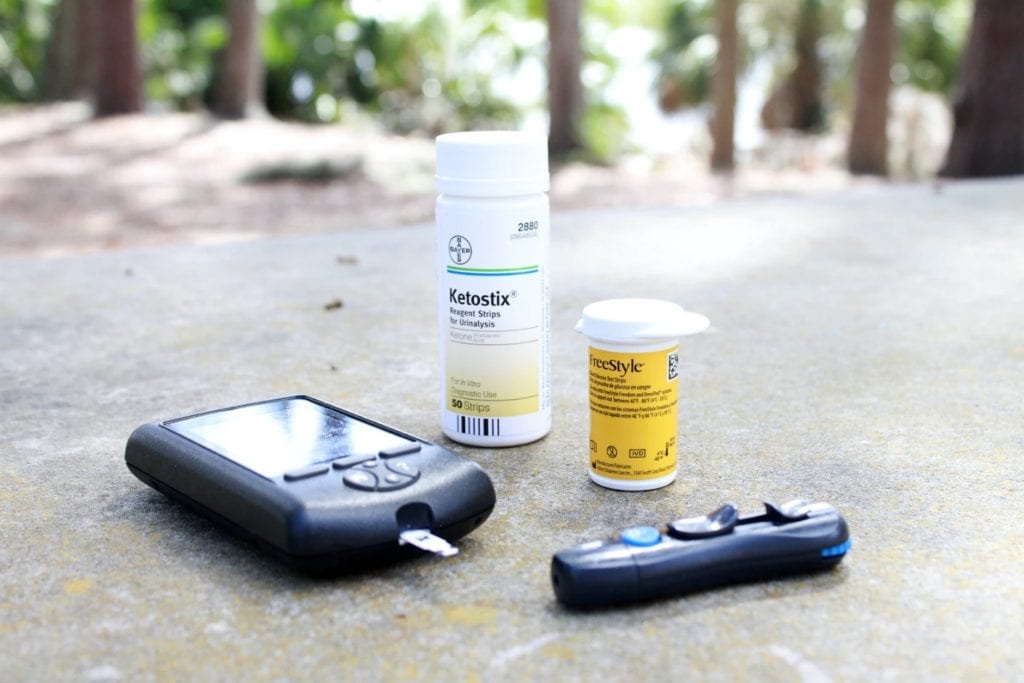
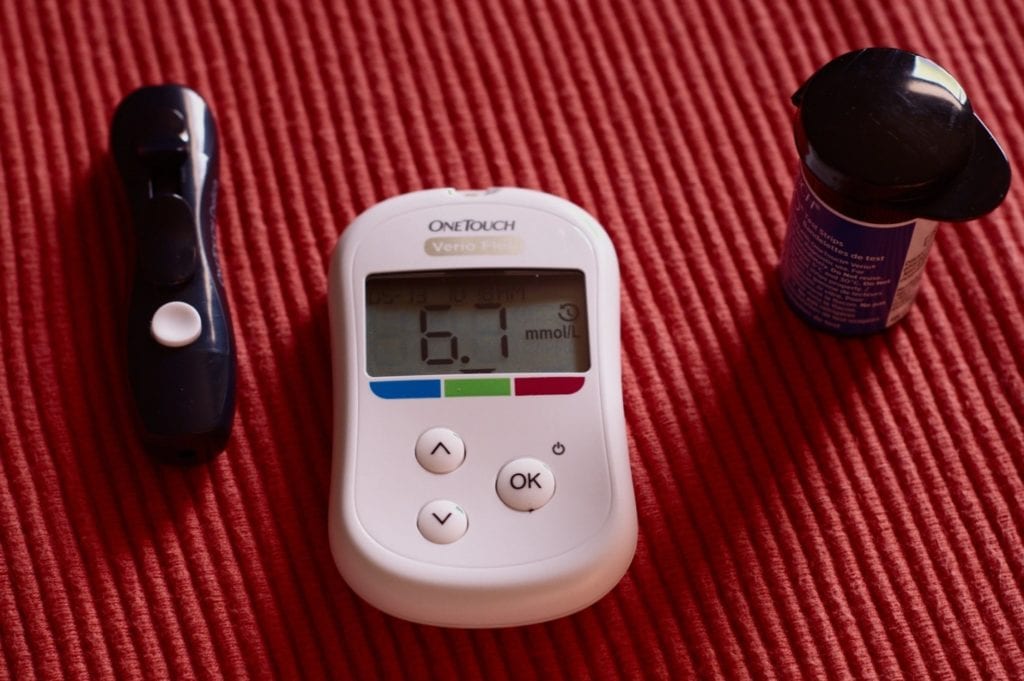
- A glucometer or glucose monitor is a device that measures blood sugar levels.
- Glucose testing strips are small plastic strips where a droplet of blood is placed to check the blood sugar levels. Test strips are disposable. It means that you use a new one every time you check your blood sugar. The number of times you check your sugar is decided by your doctor depending on the type of diabetes you have. If you have type 1 diabetes, you can utilize it 10 times a day and twice a day for type 2 diabetes. Test strips can be bought at a pharmacy or from a trusted online seller, and you can also sell extra test strips if you have an excessive supply of them. So nothing is put to waste.
- Lancing devices are small needles that prick the skin to get a blood sample.
- The kit case makes your glucometer handy.
- Insulin is a hormone taken by type 1 diabetes patients. It permits the cells to let in the sugar from the blood. It is self-administered with various devices. The devices are:
- Syringes are of different sizes and varying needles. Shorter needles produce less sting when injecting. The disadvantage is it takes the insulin longer to work.
- Insulin pens are easier to use than syringes. It has two necessary forms. One is disposable that contains a prefilled cartridge, and is thrown away after use. The other is reusable that replaces the empty cartridge with a new one.
- Insulin pumps. Insulin pumps are computerized devices used by patients with type 1 diabetes. Insulin pumps can be of two types: traditional insulin pumps and insulin patch pumps. The difference between these insulin pumps is the reservoir placement and how it is delivered inside the body. The conventional insulin pump is via infusion set, while the pump patch is through a small cannula.
- Inhalable insulin. It is like an inhaler used by people with asthma. It is usually taken in before meals. It contains rapid-acting insulin, which is pre-measured. The patient inhaled the insulin powder into the lungs; then, it penetrates the blood through tiny blood vessels.
- 6. A ketone test kit examines the blood or urine to monitor ketones’ levels, chemicals made in the liver when the body is not producing insulin to change sugar into energy. The fats are turned into ketones that are sent into the bloodstream as another source of energy. It has to be tested since people with diabetes can speed up its production leading to diabetic ketoacidosis, critical if not treated immediately.
- 7. Other Essentials can include any of the following:
- Logbook makes monitoring easier in controlling your blood sugar levels. You can also record your type and dosage of insulin, food and carbohydrate consumption, and the exercise’s type and duration.
- Glucose tablets are fast-acting sugar pills that can be taken when sugar is low.
- Glucagon shot kits is an emergency kit during severe incidents of hypoglycemia. Glucagon maintains the blood glucose levels for the body to perform well when the glucose level is low. It motions the liver to discharge glucose into the blood.
- Weighing Scale can help you supervise your nutrition and weight. Managing your weight means handling the status of your blood glucose and blood pressure.
- Diabetes Tracking Apps are modernized means of monitoring and managing diabetes with the aid of smartphones. It is a replacement of the glucose meters and traditional logbooks. A patient with the recommendation of their healthcare provider may opt for an app that provides better services with the considerations of its pitfalls. Based on Kebede and Pischke (2019) study, among the self-care components: blood glucose monitoring, general diet, and physical activity, app users were significantly higher among diabetes than the non-users.
- Emergency supplies are prepared for the rainy seasons or unexpected circumstances like calamities. It is better to have diabetes pills, insulin, extra batteries, quick sources of glucose, foods, and water stored in a water-proof container. See to it that it can last for three days. You can also add a medical alert ID and contact information.

Diabetes management is a challenging task for a diabetic patient. Several factors have to be thoroughly watched for so that food, physical activity, and medications are within the recommended range of a health professional. With the aid of devices readily available in the market, diabetes management has never been this effective and hassle-free.

